
It provides zero control and has low overhead. TFTP only allows unidirectional file transferring.
#Tftp client example full
Instead of using the full TCP implementation, TFTP relies on the connectionless and simple UDP transport over port 69. It attempts to over-simplify and downsize the functionality of FTP.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a simple file transferring mechanism developed as a “lighter” version of FTP.
#Tftp client example how to
We’ll learn how TFTP works, and how to set it up on the client and server.
#Tftp client example windows
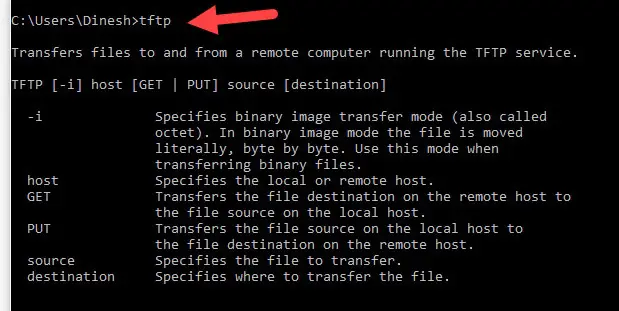
In this step-by-step tutorial, you’ll learn how to set up and configure TFTP on Windows 10. Of course, having no overhead is terrific, but there is a downside it does not provide any encryption and authentication mechanisms.Īlthough TFTP has no built-in security, network admins use it for simple and fast file transfers within LANs.Īnd best of all, it can be used for remote connections by hardening its security with the right server/client software. TFTP is simple on its own and does not need any sophisticated messaging to work. Source base, with added patches by Markus Gutschke and Gero Kulhman.Network admins use TFTP Servers every day to transfer images, configuration files, firmware, etc. It was derived from, but has substantially diverged from, an OpenBSD These access restrictions are likely to be site- and server-specific. Therefore, the remote server will probably implement some kinds of access The TFTP protocol provides no provisions for authentication or security. Toggle packet tracing (a debugging feature.) Timeout total-transmission-timeout Set the total transmission timeout, in seconds. Rexmt retransmission-timeout Set the per-packet retransmission timeout, in seconds. Enable literal mode to prevent special treatment of the ':' character (e.g. If the remote-directory form is used, the remote host is assumed to be a UNIX system or another Hostname specified becomes the default for future transfers. Has already been specified, or a string of the form host:filename to specify both a host and filename at the same time. The destination can be in one of two forms: a filename on the remote host, if the host remote-directory Put a file or set of files to the specified remote file or directory. Put file put localfile remotefile put file1 file2 file3. Mode transfer-mode Specify the mode for transfers transfer-mode may be one of ascii (or netascii) or binary (or octet.) The default is When set, this mode prevents special treatment of ':' in filenames. A remote filename can be in one of two forms: a plain filename on the remote host, if the host hasĪlready been specified, or a string of the form host:filename to specify both a host and filename at the same time.
Get a file or set of files from the specified sources. Get file get remotefile localfile get file1 file2 file3. To use the connect command the remote host can be specified as part of the get or put commands.

Transfers thus, the connect command does not actually create a connection, but merely remembers what host is to be used for transfers. Note that the TFTP protocol, unlike the FTP protocol, does not maintain connections between Print help informationĬonnect host Set the host (and optionally port) for transfers. Once tftp is running, it issues the prompt tftp> and recognizes the following commands: Print the version number and configuration to standard output, then exit gracefully. R port:port Force the originating port number to be in the specified range of port numbers. m mode Set the default transfer mode to mode. Used to avoid special processing of ':' in a file name. Must be specified last on the command line.ĭefault to literal mode. c command Execute command as if it had been entered on the tftp prompt. Host for future transfers (see the connect command below.)Ĭonnect with IPv4 only, even if IPv6 support was compiled in. The remote host may be specified on the command line, in which case tftp uses host as the default Tftp is a client for the Trivial file Transfer Protocol, which can be used to transfer files to and from remote machines, including some very


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
